Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
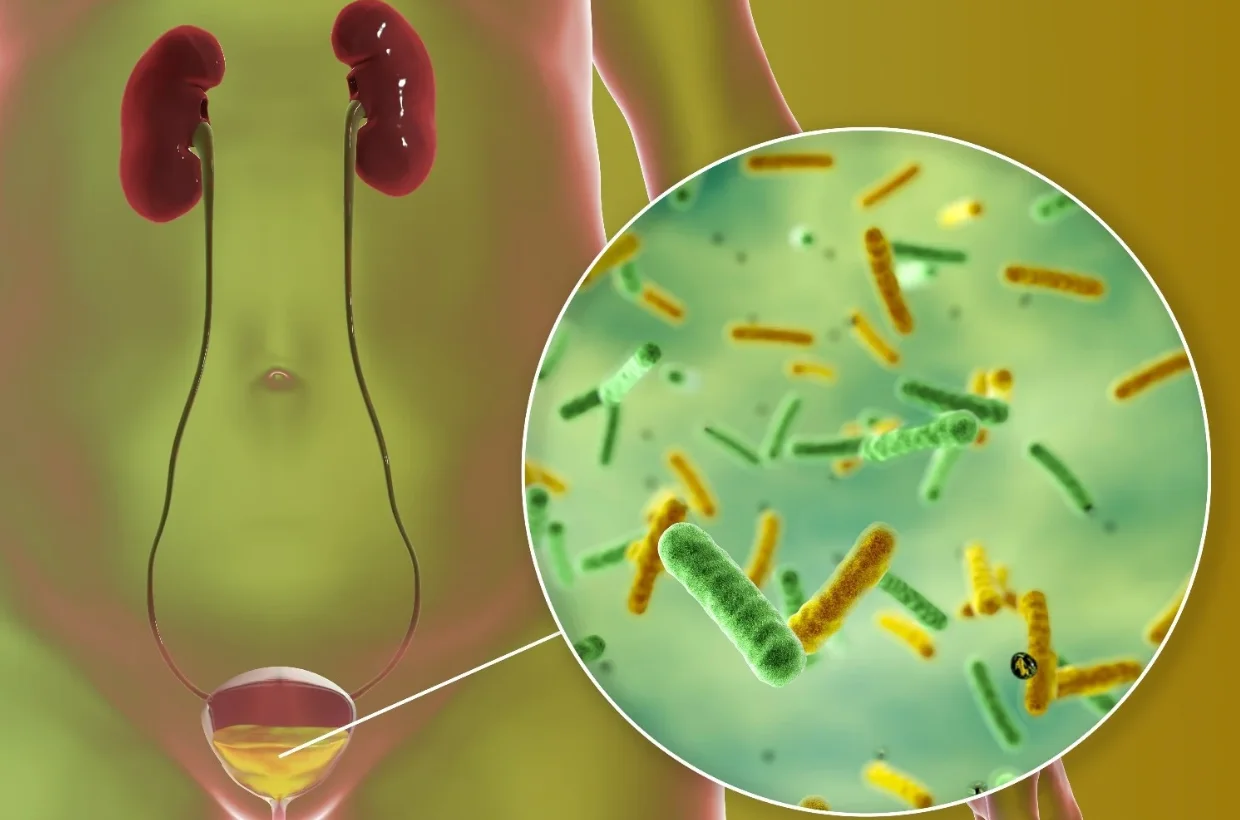
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria infect any part of the urinary system, causing burning urination, urgency, and lower abdominal pain. It is more common in women but can affect anyone. Diagnosis includes urine analysis and culture. Treatment involves targeted antibiotics and hydration. Preventive measures like maintaining hygiene and staying hydrated reduce recurrence. Prompt treatment ensures complete recovery and prevents kidney involvement.
Hematuria (Blood in Urine)
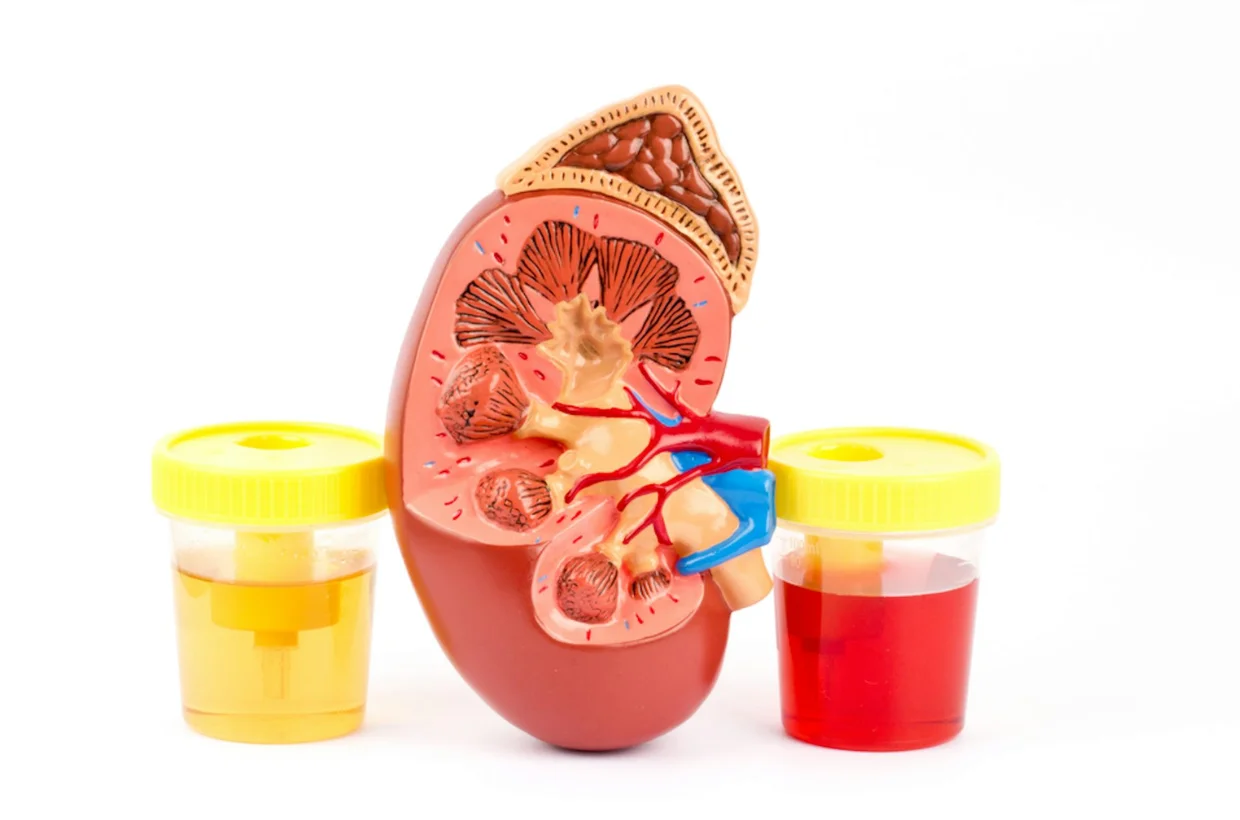
Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine, which can result from infections, stones, or tumors in the urinary tract. It may appear visibly red or be detected microscopically. Evaluation includes urine tests, ultrasound, and cystoscopy to identify the cause. Treatment depends on the underlying condition and may include medication or surgery. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent complications and ensure effective management of urinary health.

