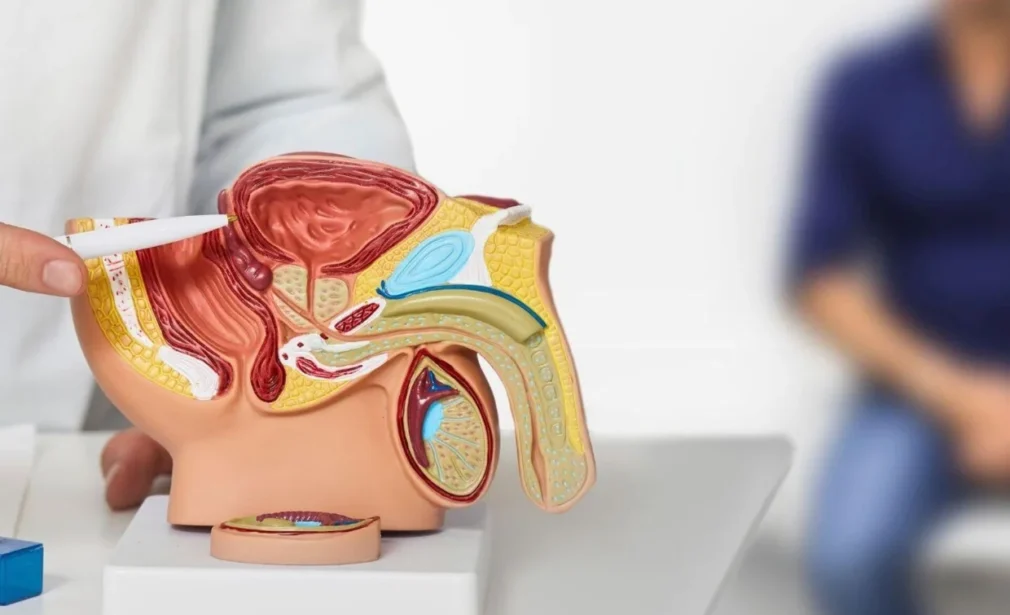
Benign Prostate Enlargement (BEP / BPH)
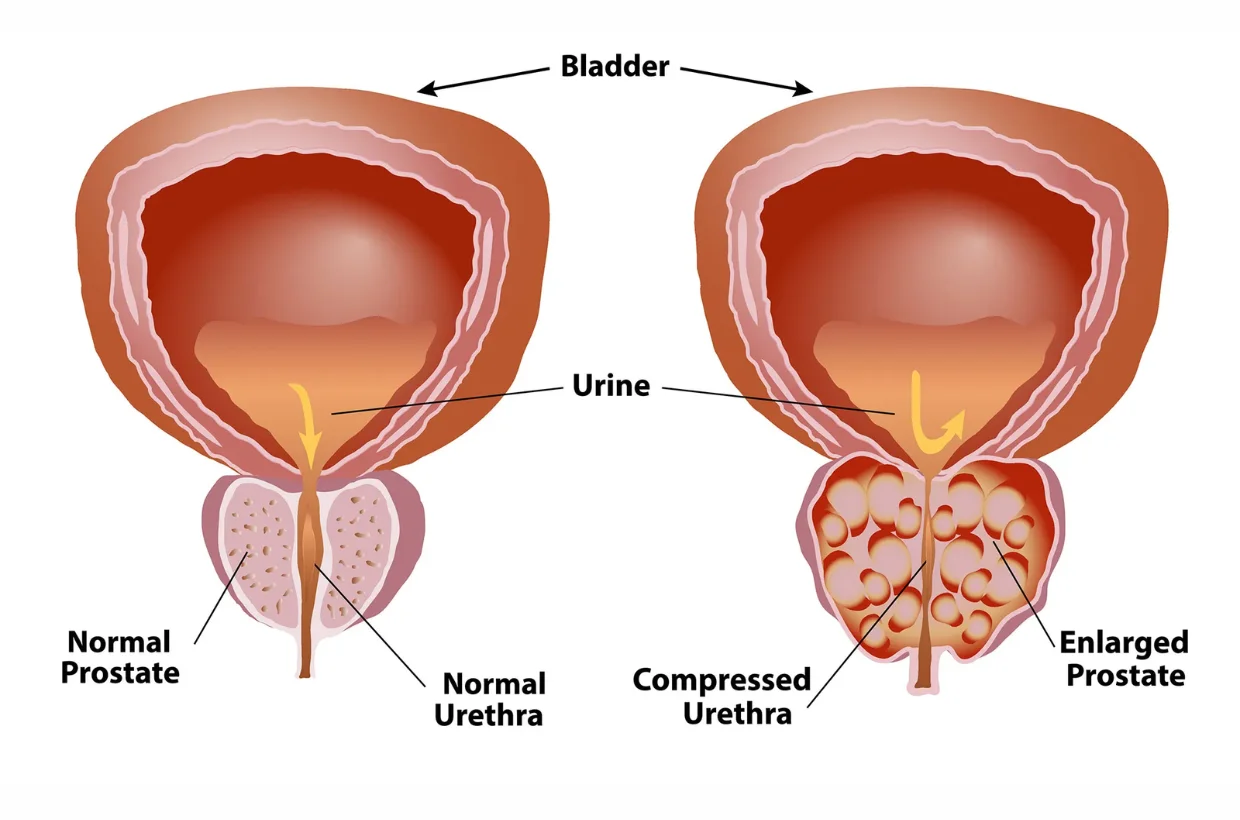
Benign prostate enlargement occurs when the prostate gland grows in size and compresses the urethra, leading to difficulty urinating, weak flow, or frequent nighttime urination. Diagnosis is done through digital rectal examination, ultrasound, and urine flow tests. Depending on the severity, treatment options include medication or minimally invasive surgery such as TURP or laser prostatectomy. Early treatment relieves urinary obstruction, prevents bladder damage, and improves overall quality of life with minimal side effects and quick recovery.
Prostatitis
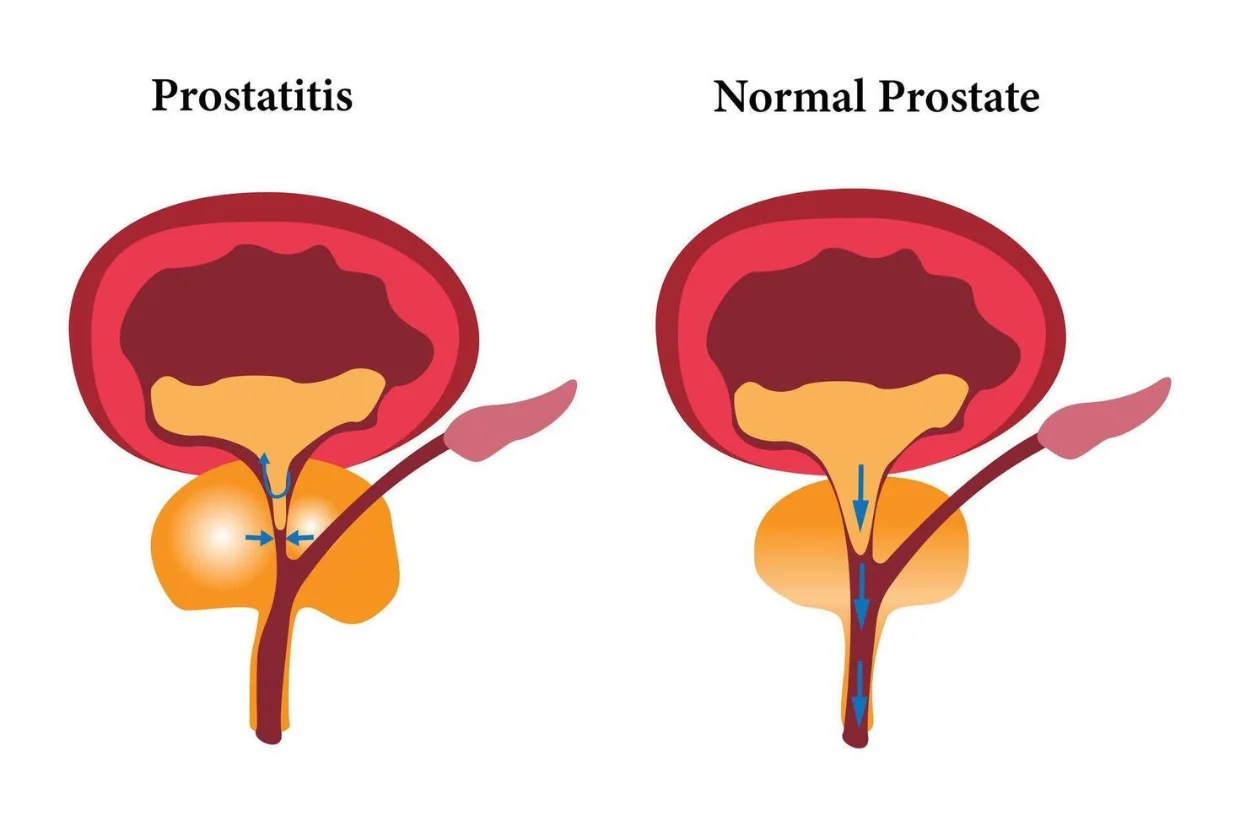
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland, often caused by bacterial infection or chronic irritation. It can lead to pelvic pain, burning during urination, fever, and discomfort during ejaculation. Diagnosis includes urine analysis, culture, and imaging to detect infection or inflammation. Treatment involves antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medication, and lifestyle changes such as increased hydration and regular voiding. Chronic cases may require long-term therapy and follow-up. Early management ensures symptom relief and helps maintain healthy prostate function.
Prostate Cancer
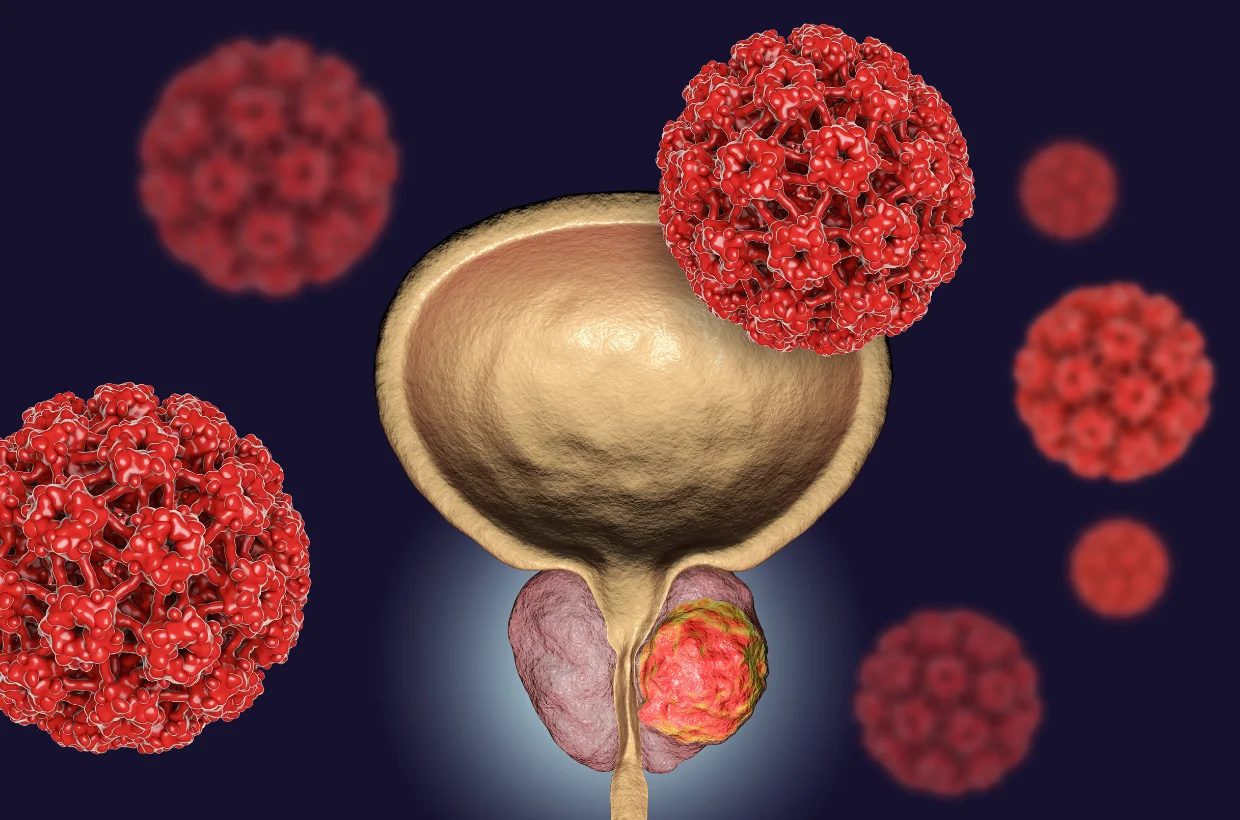
Prostate cancer develops when abnormal cells grow within the prostate gland, often progressing slowly without symptoms. Common warning signs include urinary difficulty, blood in urine, or back pain. Diagnosis involves PSA testing, biopsy, and imaging studies. Treatment depends on cancer stage and may include surgery like Radical prostatectomy, radiation, or hormone therapy. Minimally invasive options such as laparoscopic Radical prostatectomy offer faster recovery and less discomfort. Early detection and regular screening are vital for successful treatment and long-term health preservation.